In today’s world, where plastic is both a necessity and an environmental challenge, plastic granule manufacturing plays a vital role in bridging the gap between usability and sustainability. Whether you’re a startup entering the plastics industry or a curious learner wanting to know more about how your everyday plastic items begin their life, plastic granule manufacturing is where it all starts.
This blog breaks down the process, importance, and future of plastic granule production.

What Are Plastic Granules?
Plastic granules, also known as plastic pellets, are the raw materials used in making various plastic products. They come in different types — such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). These tiny bead-like particles are melted and molded into items like bottles, containers, pipes, toys, bags, and packaging materials.
There are two main sources of granules:
- Virgin granules – made from natural gas or crude oil.
- Recycled granules – made from used plastic waste.
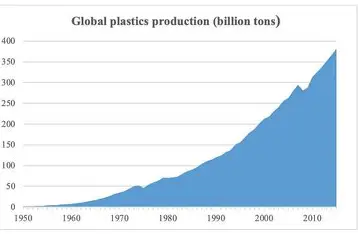
Due to environmental concerns, the demand for recycled plastic granules is growing rapidly across industries.

The Manufacturing Process of Plastic Granules
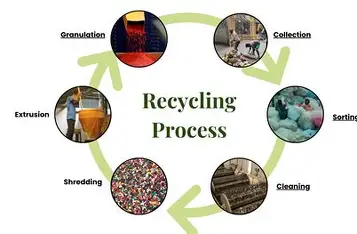
The process of manufacturing plastic granules, especially recycled ones, involves several stages. Here’s how it works:
1. Collection and Sorting
The process begins with collecting plastic waste from households, industries, or municipal sources. These are then sorted by type, color, and quality to ensure uniformity in the final product.
2. Cleaning and Washing
Sorted plastic is thoroughly cleaned to remove labels, adhesives, food residue, dirt, or other impurities. High-end facilities use automated washing systems that use hot water and detergents to ensure thorough cleaning.
3. Shredding
After washing, the plastic materials are fed into shredders or crushers where they are cut into smaller flakes. This makes it easier to melt and process them later.
4. Drying
The shredded flakes are dried to remove moisture, as even small amounts of water can affect the quality of the final granules.
5. Extrusion and Melting
The dry flakes are fed into an extruder — a machine that heats the plastic until it melts. This molten plastic is pushed through a mold or die to form thin strands.
6. Cooling and Cutting
These strands are then cooled in a water tank and cut into small, uniform pieces — these are your plastic granules. The granules are then packed and stored for use in manufacturing.
Types of Plastic Granules
There are several types of granules based on the material used:
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): Used in films, bags, and containers.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Used in bottles, toys, and pipes.
- PP (Polypropylene): Used in automotive parts, textiles, and packaging.
- PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): Used in bottles and food containers.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Used in construction, pipes, and cables.
Each type has specific qualities in terms of durability, flexibility, and resistance to heat or chemicals.
Applications of Plastic Granules
Plastic granules are used in multiple industries:
- Packaging industry: Films, wrappers, and containers
- Automotive: Interior parts, dashboards, and bumpers
- Construction: Pipes, fittings, and insulation
- Textile: Synthetic fibers and non-woven fabrics
Consumer goods: Toys, furniture, buckets, and kitchenware
Benefits of Recycled Plastic Granule Manufacturing
- Environmentally Friendly: Reduces plastic pollution and landfill waste.
- Cost-Effective: Recycling is cheaper than using virgin plastic.
- Energy Saving: Requires less energy than producing new plastic from petrochemicals.
- Job Creation: The recycling and manufacturing industry creates employment opportunities.
Resource Conservation: Limits the dependence on fossil fuels.
Challenges in Plastic Granule Manufacturing
While the benefits are significant, there are challenges:
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistency in recycled granules can be difficult.
- Contamination: Mixed or dirty plastic reduces granule quality.
- Market Fluctuations: Prices of virgin plastic often affect the competitiveness of recycled granules.
- Technology Investment: High-quality recycling equipment can be expensive.
The Future of Plastic Granule Industry
With increasing awareness around sustainability and stricter environmental regulations, the demand for high-quality recycled plastic granules is only going to rise. Innovations in chemical recycling, AI-powered sorting systems, and biodegradable plastics are likely to shape the future of this industry.
Governments are also supporting recycling units through subsidies, licenses, and waste collection infrastructure. This makes plastic granule manufacturing not just a business opportunity but a contribution toward a greener planet
Conclusion
Plastic granule manufacturing is the backbone of the plastic product industry — transforming raw or recycled materials into usable, everyday items. For businesses, it offers a profitable venture with long-term sustainability potential. For the environment, it offers a path to reduce the burden of plastic waste.Whether you’re a manufacturer, recycler, investor, or simply someone who cares about the planet, understanding this process helps you appreciate the journey from waste to wealth.
FAQs
Q1: What are plastic granules?
Plastic granules, also known as plastic pellets, are the tiny, bead-like raw materials used to manufacture various plastic products. They come in different types, such as PE, PP, PVC, and PET.
Q2: What are the two main sources of plastic granules?
The two main sources are virgin granules (made from natural gas or crude oil) and recycled granules (made from used plastic waste).
Q3: Why is there a growing demand for recycled plastic granules?
The demand for recycled plastic granules is growing rapidly due to increasing environmental concerns and the push for sustainability.
Q4: What are the key stages in the manufacturing process of recycled plastic granules?
The key stages include Collection and Sorting, Cleaning and Washing, Shredding, Drying, Extrusion and Melting, and finally, Cooling and Cutting.
Q5: What are some common types of plastic granules and their uses?
LDPE: Used in films, bags, and containers.
HDPE: Used in bottles, toys, and pipes.
PP: Used in automotive parts, textiles, and packaging.
PET: Used in bottles and food containers.
PVC: Used in construction, pipes, and cables.
Q6: In which industries are plastic granules widely used?
Plastic granules are used in multiple industries, including packaging, automotive, construction, textile, and consumer goods

